
What is Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)?
PSA technology, unlike hollow fiber membrane technology, utilizes a selective sieve material loaded into multiple adsorber beds. The sieve material is designed to selectively adsorb the waste gas while the desired gas is allowed to pass through the sieve material unaffected. The sieve material has a unique property that allows it to release any adsorbed gases once the pressure is removed for the material.
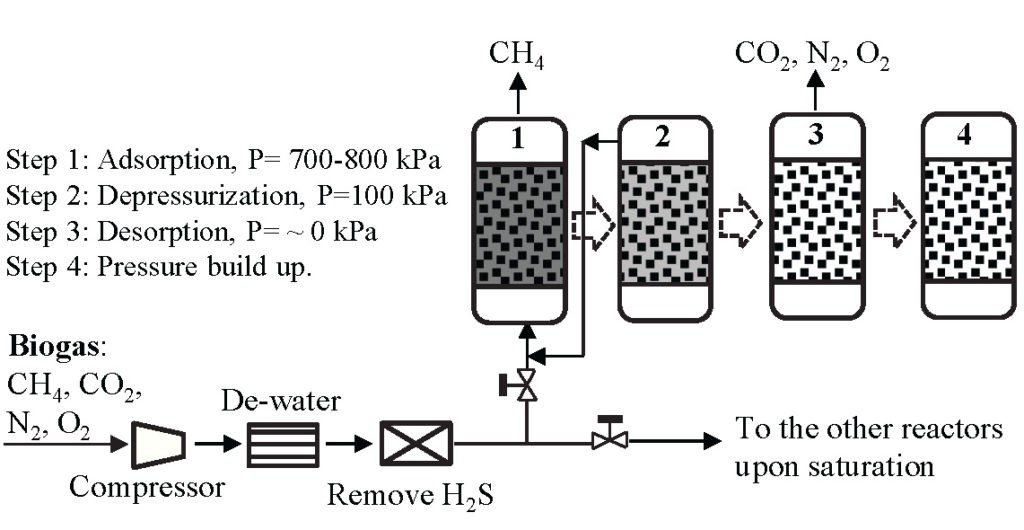
The PSA has 3 primary process steps: pressurization, adsorption, depressurization/regeneration.
Pressurization: compressed gas or air is introduced in to the bottom of the first adsorber bed, as the bed pressurizes the first adsorption bed, the unwanted gas component is adsorbed onto the surface of the selected sieve material. Normal operating pressure ranges from 100 psi(7 barg) up to 145psi(10 barg).
Adsorption: the desired product gas passes through the bed and exits from the top of the bed and is collected into a receiver tank.
Depressurization/regeneration: as this process is taking place in the first bed, the second bed is being depressurized to atmospheric pressure of a removal of unwanted gas.
This cycling is repeated on a predetermined sequence to achieve the desired output from the system.
Libra has experienced lots of PSA projects recent years with proven adsorbents and technical support, especially for Hydrogen recovery and Oxygen generation..
FULL VIDEO SOURCE: NileRed
Related products
03.
ACTIVATED CARBON FOR PSA ADSORPTION
Libra Activated carbon used for PSA adsorption, especially in Linde PSA Hydrogen recovery process.

