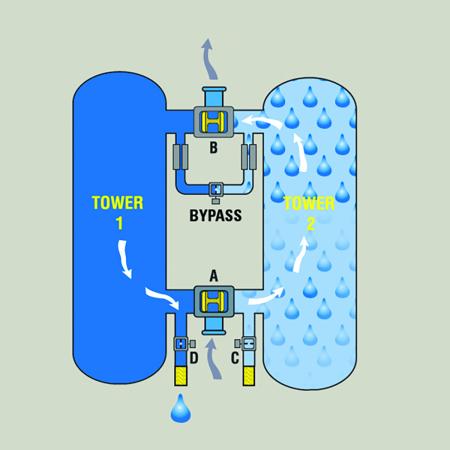
What is Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)?
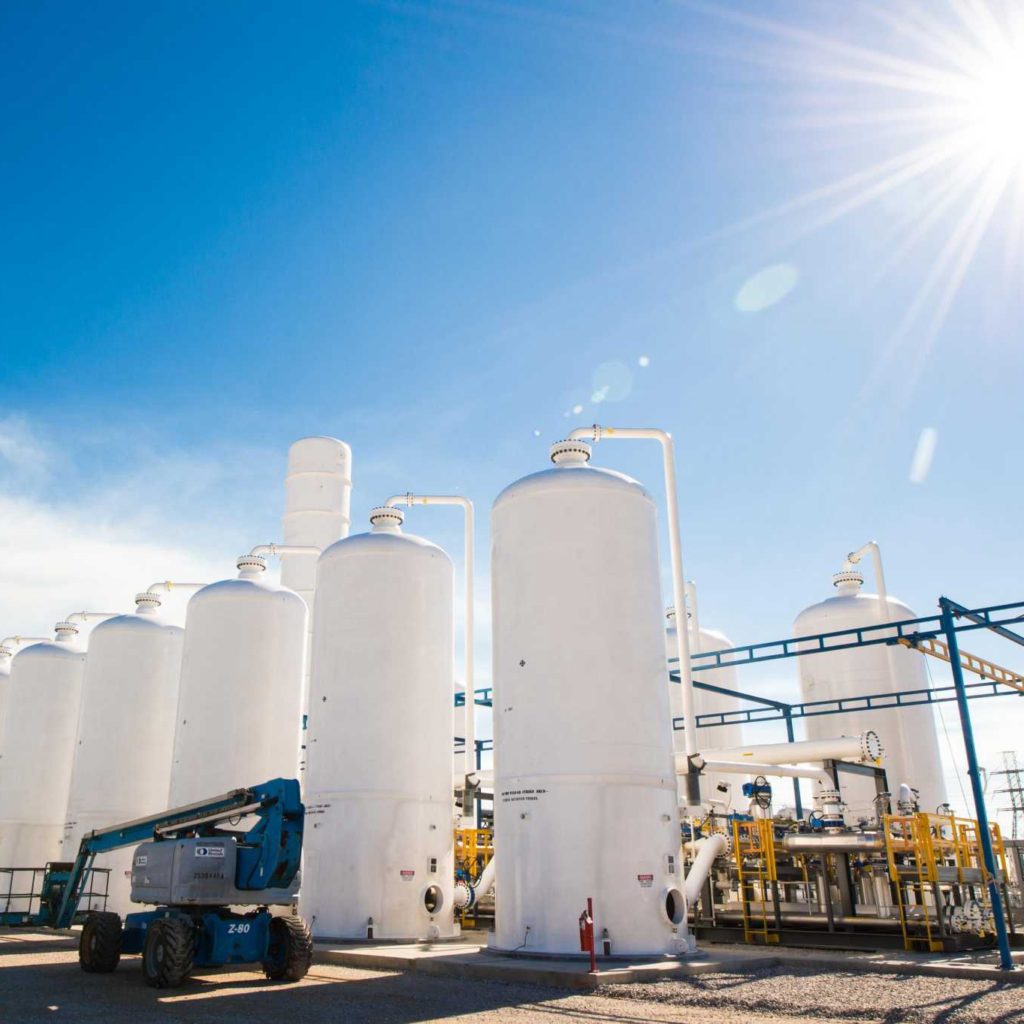
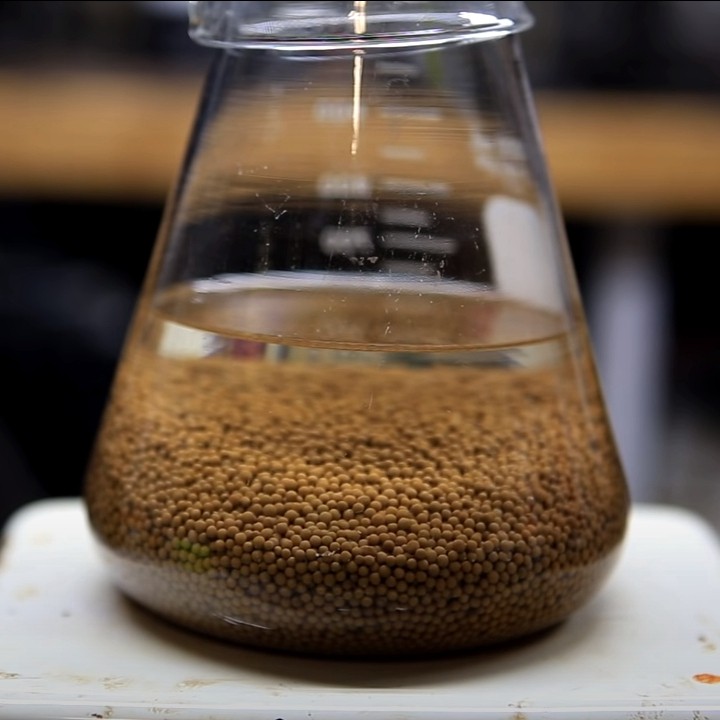
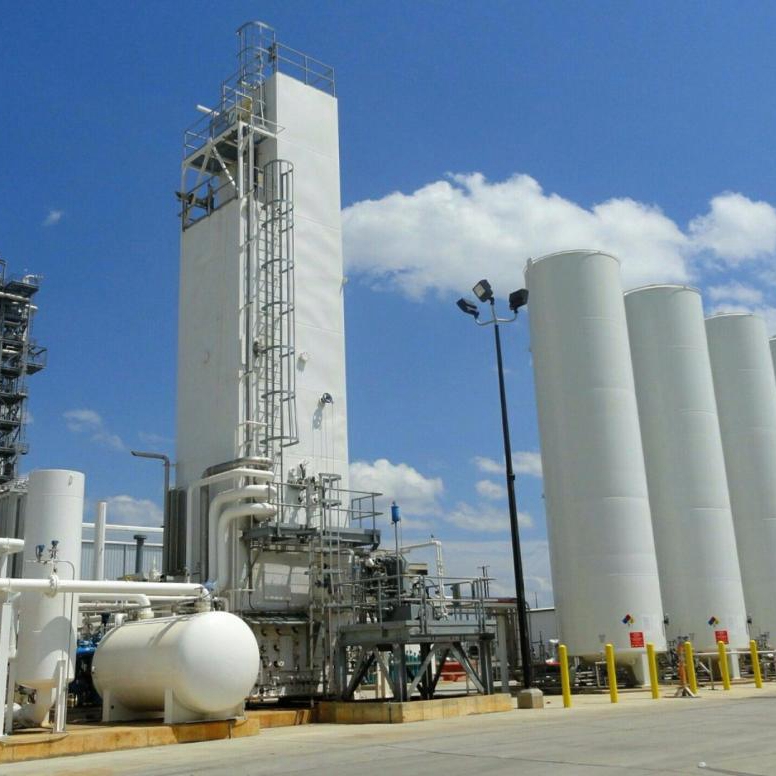
What is Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)? PSA technology, unlike hollow fiber membrane technology, utilizes a selective sieve material loaded into multiple adsorber beds. The sieve material is designed to selectively adsorb the waste gas while the desired gas is allowed to pass through the sieve material unaffected. The sieve material has a unique property that …